Image-guided therapy
iFR
Be confident in treatment and deferral decisions with Philips iFR
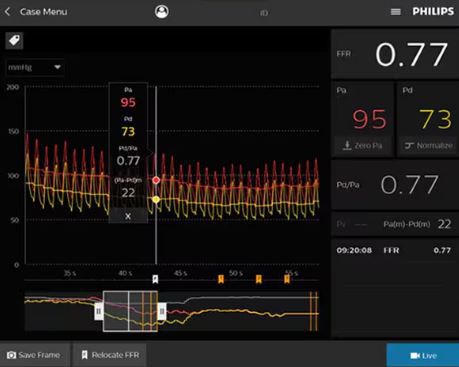
iFR is in a class of its own and is the leading hyperemia-free physiologic index for measuring pressure in diagnostic and interventional procedures. Only offered by Philips, iFR Co-registration maps the physiologic measurements directly onto the angiogram enabling more complete procedural guidance. No other resting index has an ESC and ACC/AHA/SCAI Class IA recommendation based on the high level of clinical evidence for its accuracy. Philips iFR is the Gold Standard. 1,2
Demonstrated results
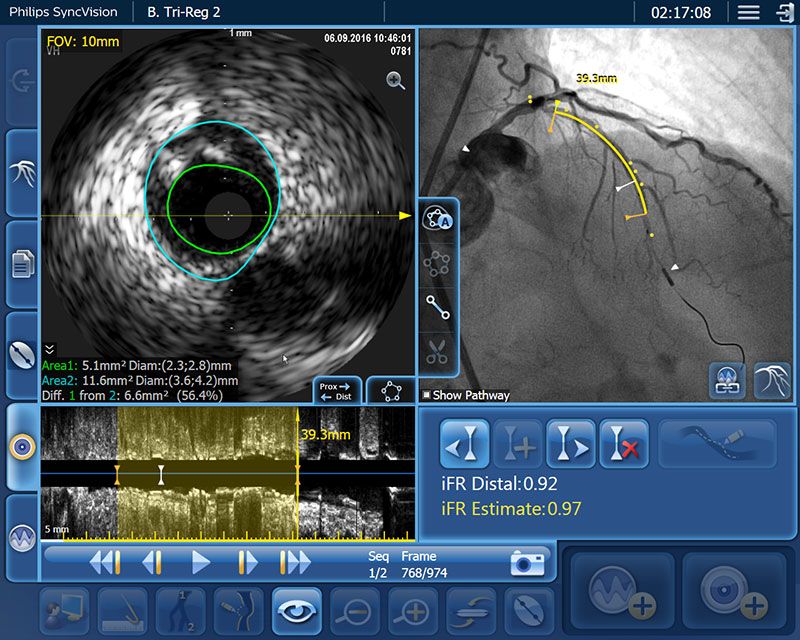
Only iFR has Co-registration for advanced physiologic guidance
Map iFR values directly onto the angiogram so you can see which parts of a vessel are causing ischemia. With iFR Co-registration there is no need for hyperemic drugs. You can automatically co-register values in seconds onto the angiogram.
- Better discern focal, serial or diffuse disease6
- Determine precise lesion severity and location7,8
- Make length measurements without a cumbersome pullback device6
- Estimate the physiologic impact of a virtual stent6
iFR Co-registration is available on the new Philips IntraSight interventional applications platform and as an upgrade to the Core systems.
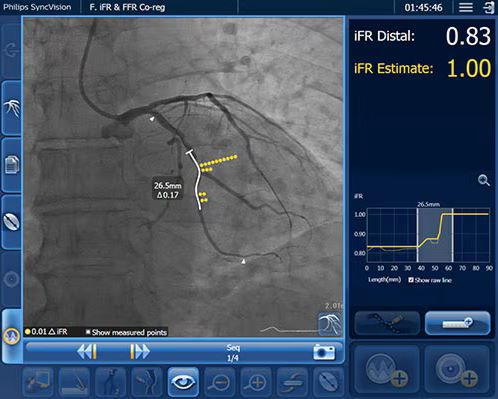
iFR Pullback technology7
iFR Pullback technology reveals the physiologic profile of the entire vessel, so when you encounter diffuse disease or serial lesions you can make informed treatment decisions.
Provides beat-by-beat iFR pressure measurements across the entire vessel, artery-by-artery
Establishes the physiological significance of each vessel and/or individual lesion (focal or diffuse)
Provides a clear view of the functional gain
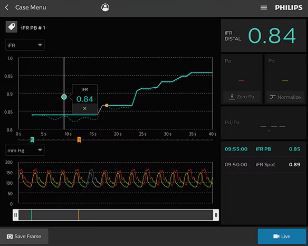
Virtually plan your PCI and predict results
Angiography provides a visual picture, but often lacks the detail needed for optimal PCI planning. Only Philips provides advanced physiologic guidance to help you determine not just whether to treat, but also where to treat, ensuring precise, patient-focused care.
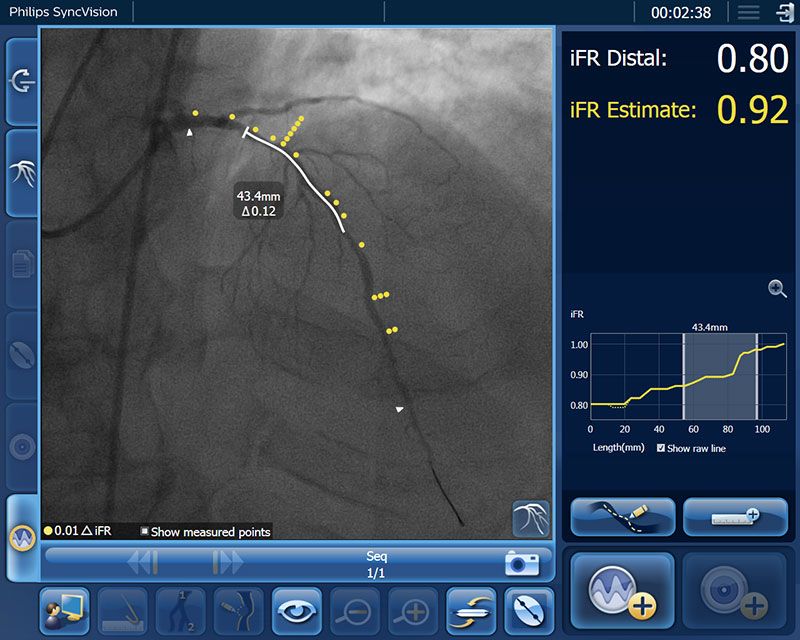
1. Identify the precise locations causing ischemia - each yellow dot signifies a 0.01 drop
2. Plan your treatment, before a stent is even placed, with a virtual stent
3. Determine lesion lengths without need for a pullback device
4. Predict physiologic gain with iFR Estimate to determine the best treatment strategies

Image gallery
Footnotes
- Neumann, F-J et al. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. European Heart Journal (2019) 40, 87–165.
- Lawton J. et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization. JACC. 2022;79(2):e21-e129.
- Jeremias A et al. Blinded physiological assessment of residual ischemia after successful angiographic percutaneous coronary Intervention: The DEFINE PCI Study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Oct 28;12(20):1991-2001.
- Patel et al. 1-Year Outcomes of Blinded Physiological Assessment of Residual Ischemia After Successful PCI. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv 2022;15:52–6.
- Berntorp et al. Instantaneous wave-free ratio compared with fractional flow reserve in PCI: A cost-minimization analysis. Int J Cardiol 2021 1;344:54-59.
- Nijjer SS, et al. Pre-angioplasty instantaneous wave-free ratio pullback provides virtual intervention and predicts hemodynamic outcome for serial lesions and diffuse coronary re-angioplasty instantaneous wave-free ratio pullback provides virtual intervention and predicts hemodynamic outcome for serial lesions and diffuse coronary artery disease. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(12):1386-96.
- Co-registration operator's manual D001336104_A_300010660481
- Data on file at Philips Syncvision co-registration validation report D001370468_B
- Davies JE, et al., Use of the Instantaneous Wave-free Ratio or Fractional Flow Reserve in PCI. N Engl J Med. 2017 24-1834
- Gotberg M, et al. iFR-SWEDEHEART Investigators. Instantaneous Wave-free Ratio versus Fractional Flow Reserve to Guide PCI. N Engl J Med. 2017 May 11;376(19):1813-1823.
- Data on file at Philips D000410086_A, D000485394_A
Disclaimer
Results are specific to the institution where they were obtained and may not reflect the results achievable at other institutions. Results in other cases may vary.